|
 |
- Search
| Asian J Kinesiol > Volume 24(4); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study is to investigate the efficacy of weight training with controlled blood flow occlusion compared to conventional resistance training, in the ageing population.
METHODS
Twenty-three healthy female subjects (aged 40-55) were randomly assigned to one of three groups; low intensity blood flow restriction training (LI-BFRT) (n = 9), conventional resistance training (RT) (n = 7) and control (CON) (n = 7). The RT group trained between 65-70% one repetition maximum (1RM) and the LI-BFRT group trained at 30% 1RM while wearing pressure cuffs inflated to 100-120% of brachial systolic blood pressure (bSBP). Relative appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM/weight), isokinetic strength and power were tested pre and post 8 weeks of training.
RESULTS
Upper limb ASM/weight increased significantly in the LI-BFRT and RT groups (both p < 0.001). Only LI-BFRT showed significant difference compared with the CON group (p < 0.01). Lower limb ASM/weight improved in both the LI-BFRT (p < 0.01) and CON (p < 0.01) groups without group differences. Lower limb flexion strength increased in the LI-BFRT and RT groups (both p < 0.01), with differences between groups (p < 0.01, LI-BFRT > RT > CON). Only RT increased extension muscle strength (p < 0.05). Lower limb flexion and extension power improved following LI-BFRT (p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, respectively), significantly greater than RT in both flexion (p < 0.001) and extension (p < 0.01).
Sarcopenia, the progressive loss of muscle mass alone [1] or in combination with increased levels of adiposity, sarcopenic obesity [2], with aging, has gained a growing body of research. This decline in health is thought to be mediated by numerous mechanisms, including alpha‐motor neuron death, altered hormone concentrations, increased inflammation, and altered nutritional status [3], contributing to the prevalence of disease and increased mortality. Sarcopenia, has been associated with a greater risk of frailty, falls and disability [4], in addition to cardio-metabolic risks, and may induce obesity, increasing the risk of developing debilitating functional limitations [5,6]. This therefore, necessitates comprehensive and efficacious interventions that are also population specific.
Resistance training (RT) is one of the most consistently effective and safe approaches to combating sarcopenic obesity, by attenuating muscle loss, improving bone mineral density, lean muscle mass, ameliorating aerobic conditioning and strength and enhancing functional ability. RT at high intensity mechanical loads, specifically recommended at >70% 1 repetition maximum (RM) [7], tend to optimize beneficial adaptations. However, orthopedic issues and cardiovascular disease, often suffered by older adults, contraindicate RT of the affected joints and may exacerbate symptoms. Nonetheless, training below 65% 1RM seldom elicits increases in muscle size or strength [8]. Blood flow restiction training (BFRT) has been reported to elicit similar muscle cross-sectional area (CSA) and strength gains as traditional RT (>70% 1RM) in male [9-11] and female subjects [12] at lower intensities. BFRT involves the full occlusion of venous blood flow by applying a pneumatic cuff, band or strap proximal to the trained muscle, but allowing for free flow of arterial blood. At low intensities (LI) of 20-30% 1RM, studies have shown LI-BFRT to significantly improve hypertrophy [13], induce an approximately 3 times greater secretion of growth hormone (GH) compared to traditional RT (~70-80% 1RM) [14-16], and maintain improvements in strength after 3 weeks of detraining [17]. Additional benefits of LI-BFRT derive from its use of low mechanical loads allowing a shorter recovery time [18], minimal muscle damage [13] and therefore permitting a higher frequency of training.
In general, women participate in physical activity or exercise with depending various motivators and context preferences [19]. However, women would participate in irregular and less frequent participation than with physical barrier and time barrier [20]. Moreover, as Korean middleaged Women have marked gender differences in social support, motivating factors, and preferences for their participation [21], it cause vicious cycle to obtain health benefits by exercise. So it would be proper guidance for Korean middle-aged women to suggest safer, and less patient intervention is more effective preferable.
The current challenge for LI-BFRT is finding safe, tolerable and accessible methods of applying the restriction to a limb, without completely occluding arterial blood flow, and ensuring comfort and ease of use. The greatest variables between studies have been in the cuff size and pressure, used to induce an effective but safe level of restriction, minimize perceived exertion and pain, and optimize exercise volume. The vast range of cuff applications has produced numerous disparities within the research, leaving BFRT methodologies open to debate. Research is also sparse into LI-BFRT applied to the middle aged (aged 40+) and female populations. Thus, the current study will investigate the effects of LI-BFRT with low cuff pressures on body composition, lower limb muscular strength and power in middle aged women.
Twenty-three females aged 40-55 years were recruited to participate in this study. Subjects whom suffered with hypertension, hypotension, coronary artery disease or diabetes were excluded from the study. All subjects were physically active taking part in moderate aerobic exercise (1-2 times per week). Subjects had not partaken in any previous resistance training prior to the exercise intervention. All participants completed a written informed consent to participate in this study.
Considering exercise volume and tolerability for middleaged women [9,22], both experimental groups performed the same 4 training movements: Dumbbell hammer curls (biceps); Cable push-downs (triceps); Leg extensions (quadriceps); and Leg curls (hamstrings). All exercise conditions were carried out at a consistent speed without strict restrictions on training time. Professional fitness trainers monitored and guided each exercise session to ensure safety and proper training technique.
:Low-Intensity Blood Flow Restriction Training
The assigned resistance exercise program was performed for 8 weeks with blood flow restriction applied using an 8 cm cuff, design by Kyungsung University Researchers (KCCuff Version 1) on the proximal upper extremities and proximal lower extremities <Table 1>. Mean blood pressure was calculated after measuring blood pressure three times. Prior to testing, a pilot test was carried out during which the aforementioned exercises were prescribed to all participants with varying levels of cuff pressure. Moderately trained males were asked to attempt exercising at 30% 1RM using a range of cuff pressures (100% - 180% bSBP), and to give feedback on the tolerability and intensity of working at such cuff pressures. From this, an appropriate range of pressures were assigned for participants to try and give the same feedback. Upper and lower extremity cuff pressures were set at 100% and 120% of subjects’ individual brachial systolic blood pressure (bSBP), respectively. Complaints of pain, discomfort and skin irritation associated with higher cuff pressures, and participants’ perception of an adequate stimulus for exercise, were also used considered when choosing pressures.
Maximum muscle strength, 1RM, was derived from the formula proposed by O’Conner et al [23]. Based on the principal of progressive overload, 1RM was measured again on the 5th week, and reassigned at 30% of the subsequent measurement. According to the American college of sports medicine [7] muscle strength training protocols, the program was performed 3 times a week for a total of 50 minutes, comprising pre-exercise, main exercise and cool-down exercise. 30 minutes of main exercise was performed with each specific exercise carried out for 5 sets, with the 1st set at 20 reps and the 2nd - 5th sets at 15 reps. 1 minute, and 1 minute and 30 seconds of rest was carried out between sets for the upper and lower extremity, respectively. The cuff remained inflated throughout the entire exercise session including rest periods, and was altered if discomfort, dizziness or movement restriction occurred.
Considering RT recommendations [7] and the middleaged female cohort, intensity was set at 65~70% of 1RM, dependent upon level of pain, ability to complete all movements at maximal effort and a required full ROM. RT consisted of 4 sets in total: 1st set (warm-up), low intensity, 20% 1RM with 20 reps; 2nd - 4th set, high intensity, 65~70% 1RM with 12 reps. Rest periods between sets lasted 30 seconds for upper extremities and 60 seconds for lower extremities. In order to induce gradual overload, 60~65% 1RM was recalculated and reassigned on the 5th week. Apart from the differences in intensity to the LI-BFRT group, frequency, exercise period and time were all the same <Table 1>.
The 23 participants were randomly assigned to one of three groups, 9 to the LI-BFRT group, 7 to the resistance training (RT) group and 7 to the CON group. Subjects performed 8 weeks of their respective training program. 1 week prior to the training program, participants completed a familiarization session which included the taking of pre-test baseline measurements of resting blood pressure and familiarization with LI-BFRT and resistance training exercise techniques. Pre and Post-test measurements took place from 9 a.m. in the mornings (physique and body composition) to 3 p.m. in the afternoons (strength) within 7 days prior to the 8-week training program and within 3 days after completion. Subjects were told to refrain from smoking and/or consumption of alcohol during the testing and experimental period.
Height and weight were measured using the Jenix DS-102 Hologic (USA). Subjects were instructed to maintain a straight, upright posture after which height was measured to one decimal place and weight measured to the nearest 0.1kg.
Measurements of appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM/weight) were carried out at the Medical Centre for Health Promotion (Busan, Korea) using the DEXA (Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry, Discovery QDR Hologic, USA) on both limbs. Subjects were fitted with robes and had their measurements taken by professionally trained assistants, taking 15 minutes for the entire body.
Isokinetic strength and power measurements were taken using a Biodex machine (Biodex system 4 Pro, Biodex. USA). With subjects seated, the dynamometer was adjusted to match the rotational axis of the worked extensors and flexors. Participants were encouraged to remain seated, not moving other body parts except for the pelvis, with additional external force (straps) applied to prevent movement of the femoral site and chest. Attachments were used to accommodate for knee leg length ranges of motion. Isokinetic knee flexion and extension were measured in the anatomical position, through 90 °- 0 °and again from 0 °- 90 °whilst being adjusted for hyperextension. These values were then recorded for consistent use throughout the remaining testing period. Load speeds of 60°/sec and 180°/sec were performed on the lower limbs to assess both muscle strength and power, respectively. All measurements concerning upper and lower limb ASM/weight and lower limb strength and power, were evaluated within 7 days of starting the program and 3 days of completion.
All statistical analysis was conducted with Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS Windows Version 28.0). Descriptive statistics (mean and standard deviation) were used to report on the measurements of each variable. To evaluate training effects a Paired-T test was used on all dependent variables. An ANCOVA was used to test the differences between the training group conditions, and Helmert contrast was used as the contrast method. Statistical significance was set at α=.05.
Participants mean age, height and weight were 47.35 ± 4.58 years, 159.96 ± 3.60 cm and 56.73 ± 4.83 kg, respectively <Table 2>. Blood pressure readings, prior to testing averaged 121.13 ± 10.51 mmHg and 75 ± 9.05 mmHg for systolic and diastolic pressures, respectively. There was no statistical difference between pre and post weight measurement values in all three groups.
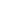
In regard to changes in muscle mass, upper limb ASM/weight showed significant increases in both the LI-BFRT (p < 0.001) and RT groups (p < 0.001), with significant differences between groups (CON<BFR, p < 0.01). LI-BFRT, along with the CON group induced a significant increase in lower limb muscle mass (p < 0.05) <Figure 1 and 2>. There were, however, no differences between groups.
Muscle strength was shown to significantly improve in the LI-BFRT (p < 0.01) and RT (p < 0.01) group at 60°/sec Peak Tq of flexion, with a significant difference between groups (p < 0.01, LI-BFRT>RT>CON) <Figure 3 and 4>. However, only RT elicited a significant increase in muscle strength at 60°/sec Peak Tq of extension (p < 0.05), without any between-groups differences. Muscle power improvements at 180°/sec Peak Tq were seen for both flexion and extension in the LI-BFRT group (p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, respectively). In addition, there were significant differences between conditions for both flexion and extension, with LI-BFRT inducing significantly greater improvements than both the RT and CON groups for flexion (p < 0.001) and extension (p < 0.01) movements <Figure 5 and 6>.
This study provided support for the use of LI-BFRT, with intensities as low as 30% 1RM, to significantly improve muscle strength and power, and ASM/weight in middle-aged women. The present study used relatively low pressures of 100% and 120% of subjects’ bSBP (~157.3 mmHg). Such arbitrary methods have been criticized in previous literature as they do not account for individual limb size and may increase the risk of complete arterial occlusion [24]. However, further to the convenience of prescribing standardized pressures, Yokokawa et al [25] reported 120% bSBP as a safe and tolerable pressure to elicit significant physical fitness improvements in the elderly population, of whom we may predict, are at a higher risk of injury and complication than middle-aged women. In addition, as used in this study, one’s perception of intensity of exercise (i.e. cuff pressure) using LI-BFRT has been shown to be a good indicator of arterial restriction and suitability of exercise [13]. Despite the present study not reporting on pain levels, perception of intensity was deemed tolerable (ascertained pre-test), so much so that subjects were able to perform the assigned LI-BFRT exercise as required, without pain. It was thus demonstrated that safe pressures coupled with manageable intensities of exercise can elicit significant improvements in muscle strength, power and mass.
Cuff size is most likely a determining factor in the improvements of ASM/weight and strength with LI-BFRT in the present study <Table 3>. A study showed that when using the same protocol, an increase in elbow flexion strength was observed after training with a 7cm cuff, whereas a 12cm cuff induced no strength gains [9] (possibly as a result of complete arterial occlusion). 4cm, 5cm and 9cm width cuffs inflated to 160-240 mmHg have also been shown as effective combinations of pressure and cuff size for strength and hypertrophic gains following knee extension exercises [22]. However, none of these studies were completed using LI-BFRT on females, and all were carried out on subjects younger than 25 years [24]. Shaw and Murray [26] put forward that narrow cuffs may not induce a true restrictive pressure due to pressure loss with increasing limb tissue depth. Therefore, considering that women typically have smaller limb dimensions than men [27], the current study hypothesized that lower pressures would be adequate to induce a significant training effect. This was previously demonstrated by Takarada et al [15], when following a 16-week program of LI-BFRT at ~50-30% 1RM, using an 9cm cuff inflated to ~110 mmHg, significant increases in isokinetic strength and muscle cross-sectional area in middle aged women were observed. The present study not only used a narrower cuff (8cm), but also a shorter program duration (8 weeks) and lower exercise intensity (30%) yet increases in lower limb muscle strength and power were observed, and almost always greater or equal to RT <Table 4>. Hence, it may be deduced that the absolute pressure needed for muscular adaptation, with narrow to moderate cuffs in an aging female population, is much lower than previously demonstrated in men and women. Furthermore, the tolerability of LI-BFRT allows for untrained individuals to engage in exercise they may have typically avoided. Such benefits become pertinent when considering that physical discomfort is a common barrier in health behaviors of the aging Korean population [28].
To understand these adaptations, research suggests that increased cellular swelling may be a major mechanism [29], caused by the pooling of blood, an accumulation of intramuscular metabolites [30] and reactive hyperemia, ultimately stimulating various anabolic-signaling pathways [31, 32], resulting in a greater increase in growth factors [15], epinephrine [33] and norepinephrine [22, 15]. Accumulation of blood lactate concentration [34], significant elevations in post-exercise IGF-1 [34, 35] and the concomitant decrease in myostatin [36], have all been linked to the strength and mass improvements following LI-BFRT. However, it is important to note that there are disparities in the research regarding these mechanisms and their exact influences on the stimulation of physiological adaptations following LI-BFRT [37-39]. Significant improvements in mean power at 180°/sec Peak Tq were also observed in the present study <Table 4>, and greatest in the LI-BFRT group. This may be due to the concomitant increase in muscle strength, as was observed in this study, or the preferential recruitment of type II muscle fibers, via stimulation of group III and IV afferent fibers following reported changes in intramuscular venous pH [30], venous oxygen, carbon dioxide partial pressure and venous lactate concentration [33]. Furthermore, an indirect link between LI-BFRT and increased recruitment of type II muscle fibers was shown by an increased S6K1 phosphorylation, which occurs primarily in fast twitch muscle fibers, in the BFRT group following a “work matched” resistance exercise program [32]. Differences in protocol, particularly duration of effort, program length, exercise to failure [40], cuff size and pressure may account for the extent of physiological changes. Nonetheless, the inconsistencies in research indicate the likelihood of other mechanisms, beyond lactate accumulation and metabolic acidosis, playing a role in the adaptational responses to LI-BFRT. Limitations of the present study include the small sample size. The pre-test drop-out rate (average of 3 persons per group), due mainly to difficulties in performing the resistance training element of the program, meant sample size was small and may have affected statistical significance. Future studies may therefore want to address optimization of LI-BFRT by further investigating acute versus long term adaptations, intermittent versus continuous training and the potential changes to body fat percentage following LI-BFRT. The absence of significant change in body weight <Table 5> may be due to very slight reductions in lower limb body fat <Table 6, 7>, compensated for by increases in lower limb muscle mass, as demonstrated in the present study.
In alignment with prevailing BFRT research, our results demonstrate that improvements in muscle strength, power and muscle mass are achievable at a greater or tantamount degree to that of RT, though at a much lower intensity, indicating a direct effect of blood flow occlusion on muscle growth. Such an exercise approach may be a safe and efficacious preventative intervention in the case of sarcopenic obesity and its association with more severe health issues.
LI-BFRT lends itself well to home-based training programs and, for those to which high-load resistance exercise is a contraindication (e.g. arthritic or osteoporotic patients), a tolerable intervention. The middle-aged female population may find themselves without the time or energy to partake in RT, thus such low-impact activity appears more accessible and pragmatic.
Figure 1.
Upper Limb ASM/Weight before and after LI-BFRT, RT and CON group activity performed for 8 weeks.
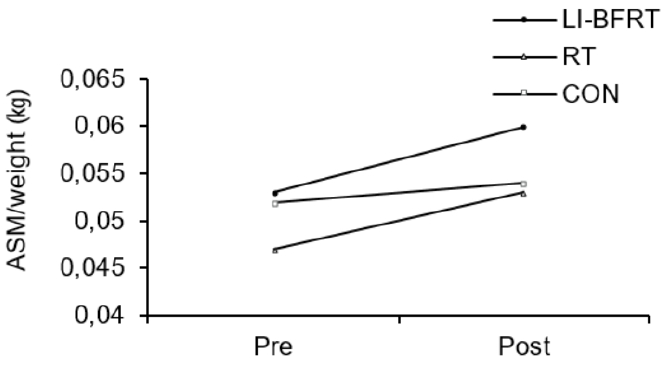
Figure 2.
Lower Limb ASM/Weight before and after LI-BFRT, RT and CON group activity performed for 8 weeks.
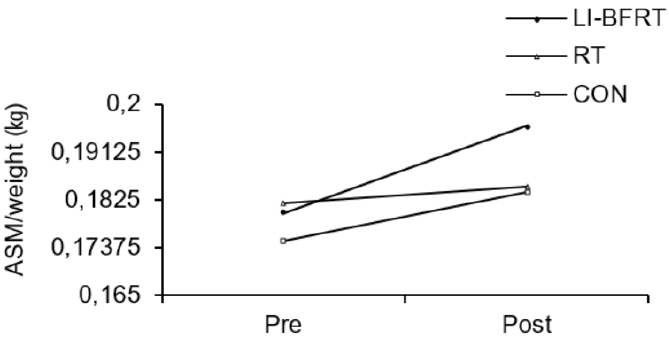
Figure 3.
Lower Limb muscle strength measured at 60°/sec extension before and after LI-BFRT, RT and CON group activity performed for 8 weeks.
Figure 4.
Lower Limb muscle strength measured at 60°/sec flexion before and after LI-BFRT, RT and CON group activity performed for 8 weeks.

Figure 5.
Lower Limb muscle power measured at 180°/sec extension before and after LI-BFRT, RT and CON group activity performed for 8 weeks.
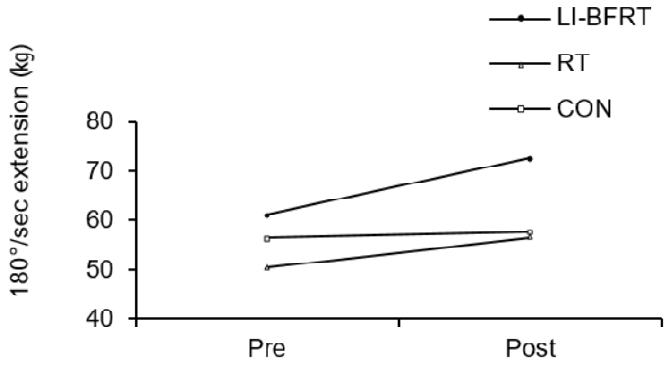
Figure 6.
Lower Limb muscle power measured at 180°/sec flexion before and after LI-BFRT, RT and CON group activity performed for 8 weeks.
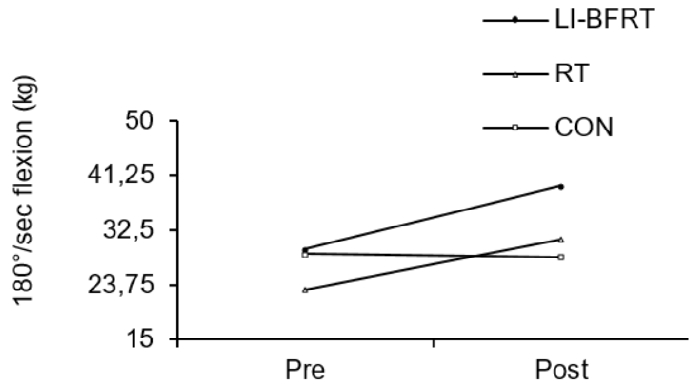
Table 1.
Eight-week LI-BFRT and Resistance Training (RT) Programs
Table 2.
Participant characteristics
Table 3.
Changes in appendicular skeletal muscle mass.
| Pre | Post | Between Groups | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upper body ASM/weight (kg) | |||
| LI-BFRT | .053±.006 | .060±.003*** | CON < LI-BFRT † |
| RT | .047±.004 | .053±.005*** | CON < RT |
| CON | .052±.004 | .054±.004* | RT < LI-BFRT |
| Lower body ASM/weight (kg) | |||
| LI-BFRT | .180±.012 | .196±.021* | CON < LI-BFRT |
| RT | .182±.019 | .185±.018 | CON < RT |
| CON | .175±.017 | .184±.017* | RT < LI-BFRT |
Table 4.
Changes in muscle strength and power variables.
| Pre | Post | Between Groups | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60˚/sec Extension Lower Limb (kg) | |||
| LI-BFRT | 106.56±25.36 | 113.57±22.81 | CON < LI-BFRT |
| RT | 81.52±20.72 | 92.51±21.63* | CON < RT |
| CON | 86.62±10.23 | 89.27±7.76 | RT < LI-BFRT |
| 60˚/sec Flexion Lower Limb (kg) | |||
| LI-BFRT | 43.44±14.18 | 53.33±10.07** | CON < LI-BFRT † |
| RT | 33.72±8.17 | 42.02±10.51** | CON < RT |
| CON | 37.60±5.22 | 39.38±5.21 | RT < LI-BFRT |
| 180˚/sec Extension Lower Limb (kg) | |||
| LI-BFRT | 61.24±17.08 | 72.77±11.20* | CON < LI-BFRT † |
| RT | 50.62±14.67 | 56.57±9.40 | CON < RT |
| CON | 56.44±6.71 | 57.52±6.67 | RT < LI-BFRT † |
| 180˚/sec Flexion Lower Limb (kg) | |||
| LI-BFRT | 29.50±9.16 | 39.54±7.16** | CON < LI-BFRT |
| RT | 23.04±8.30 | 31.08±4.38** | CON < RT |
| CON | 28.68±6.48 | 28.05±5.53 | RT < LI-BFRT ‡ |
Table 5.
Participants Weight (kg) Before and After the Experimental Period
| Group | N | Before | After | t-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LI-BFR | 9 | 61.00±6.32 | 61.11±6.90 | -0.286 |
| RT | 7 | 53.14±4.29 | 52.71±5.02 | 1.000 |
| CON | 7 | 55.95±5.15 | 56.28±5.31 | -0.530 |
References
1. Fielding RA, Vellas B, Evans WJ, et al. Sarcopenia: An Undiagnosed Condition in Older Adults. Current Consensus Definition: Prevalence, Etiology, and Consequences. International Working Group on Sarcopenia. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association. 2011; 12(4): 249–256.


2. Baumgartner RN. Body Composition in Healthy Aging. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2000; 904(1): 437–448.


4. Ryu M, Jo J, Lee Y, Chung Y-S, Kim K-M, Baek W-C. Association of physical activity with sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in community-dwelling older adults: the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Age and Ageing. 2013; 42(6): 734–740.


5. El Masri D, Itani L, Tannir H, Kreidieh D, El Ghoch M. The Relationship between Sarcopenic Obesity, Weight-Loss and Maintenance Outcomes during Obesity Management: Are Additional Strategies Required? Clin Pract. 2021; 11(3): 525–531.



6. Wannamethee SG, Atkins JL. Muscle loss and obesity: the health implications of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity. Proc Nutr Soc. 2015; 74(4): 405–12.


7. Progression Models in Resistance Training for Healthy Adults. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise. 2009; 41(3): 687–708.


8. Kraemer WJ, Ratamess NA. Fundamentals of Resistance Training: Progression and Exercise Prescription. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise. 2004; 36(4): 674–688.


9. Item F, Denkinger J, Fontana P, Weber M, Boutellier U, Toigo M. Combined effects of whole-body vibration, resistance exercise, and vascular occlusion on skeletal muscle and performance. Int J Sports Med. 2011; 32(10): 781–7.


10. Yasuda T, Loenneke JP, Thiebaud RS, Abe T. Effects of Blood Flow Restricted Low-Intensity Concentric or Eccentric Training on Muscle Size and Strength. PLoS ONE. 2012; 7(12).

11. Takarada Y, Sato Y, Ishii N. Effects of resistance exercise combined with vascular occlusion on muscle function in athletes. European Journal of Applied Physiology. 2002; 86(4): 308–314.


12. T Inagaki Y, Madarame H, Neya M, Ishii N. Increase in serum growth hormone induced by electrical stimulation of muscle combined with blood flow restriction. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011; 111(11): 2715–21.


13. Wilson JM, Lowery RP, Joy JM, Loenneke JP, Naimo MA. Practical Blood Flow Restriction Training Increases Acute Determinants of Hypertrophy Without Increasing Indices of Muscle Damage. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research. 2013; 27(11): 3068–3075.


14. Kraemer WJ, Ratamess NA, Hymer WC, Nindl BC, Fragala MS. Growth Hormone(s), Testosterone, Insulin-Like Growth Factors, and Cortisol: Roles and Integration for Cellular Development and Growth With Exercise. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020; 11:33.



15. Takarada Y, Takazawa H, Sato Y, Takebayashi S, Tanaka Y, Ishii N. Effects of resistance exercise combined with moderate vascular occlusion on muscular function in humans. Journal of Applied Physiology. 2000; 88:2097–2106.


16. Viru M, Jansson E, Viru A, Sundberg CJ. Effect of restricted blood flow on exercise-induced hormone changes in healthy men. European Journal of Applied Physiology and Occupational Physiology. 1998; 77(6): 517–522.


17. Yasuda T, Loenneke JP, Ogasawara R, Abe T. Effects of short-term detraining following blood flow restricted low-intensity training on muscle size and strength. Clinical Physiology and Functional Imaging. 2014; 35(1): 71–75.


18. Abe T. Journal of Training Science for Exercise and Sport. 2004; 16:199–207.
19. van Uffelen JGZ, Khan A, Burton NW. Gender differences in physical activity motivators and context preferences: a population-based study in people in their sixties. BMC Public Health. 2017; 17(1): 624.



20. Nishida Y, Suzuki H, Wang DH, Kira S. Psychological determinants of physical activity in Japanese female employees. Journal of Occupational Health. 2003; 45(1): 15–22.


21. Myung-Sill Chung, Ji-Ho Song. Social Support and Health Status based on Characteristics of Leisure Activity of Middle-Aged Women. Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing. 2011; 18(1): 97.
22. Abe T. Effects of short-term low-intensity KAATSU training on strength and skeletal muscle size in young men (Japanese with English abstract). Journal of Training Science for Exercise and Sport. 2004; 16:199–207.
23. Madarame H, Neya M, Ochi E, Nakazato K, Sato Y, Ishii N. Cross-Transfer Effects of Resistance Training with Blood Flow Restriction. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise. 2008; 40(2): 258–263.


24. O’Conner B, Simmons J, O’Shea P. Weight training today. St. Paul, MN: West Publishing;1989.
25. Loenneke JP, Wilson JM, Pujoi TJ. Potential safety issues with blood flow restriction training. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports. 2011; 21(4): 510–518.


26. Jørgensen SL, Mechlenburg I. Effects of Low-Load Blood-Flow Restricted Resistance Training on Functional Capacity and Patient-Reported Outcome in a Young Male Suffering from Reactive Arthritis. Front Sports Act Living. 2021; 3:798902.



27. Tuncali B, Karci A, Tuncali BE, et al. A new method for estimating arterial occlusion pressure in optimizing pneumatic tourniquet inflation pressure. Anesth Analg. 2006; Jun;102(6): 1752–7.


28. McDowell MA, Fryar CD, Ogden CL, Flegal KM. Anthropometric Reference Data for Children and Adults: the United States, 2003-2006. PsycEXTRA Dataset.
29. Eun Y, Song MS, Gu MO. Barriers to Health Behaviors in Male and Female Elderly People in Korea. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2008; 38(2).

30. Loenneke JP, Fahs CA, Rossow LM, Abe T, Bemben MG. The anabolic benefits of venous blood flow restriction training may be induced by muscle cell swelling. Medical Hypotheses. 2012; 78(1): 151–154.


31. Suga T, Okita K, Takada S, et al. Effect of multiple set on intramuscular metabolic stress during low-intensity resistance exercise with blood flow restriction. European Journal of Applied Physiology. 2012; 112(11): 3915–3920.



32. Fry CS, Glynn EL, Drummond MJ, et al. Blood flow restriction exercise stimulates mTORC1 signaling and muscle protein synthesis in older men. Journal of Applied Physiology. 2010; 108(5): 1199–1209.



33. Walker DK, Dickinson JM, Timmerman KL, et al. Exercise, amino acids, and aging in the control of human muscle protein synthesis. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011; 43(12): 2249–58.



34. Yasuda T, Abe T, Brechue WF, et al. Venous blood gas and metabolite response to low-intensity muscle contractions with external limb compression. Metabolism. 2010; 59(10): 1510–1519.


35. Takano H, Morita T, Iida H, et al. Hemodynamic and hormonal responses to a short-term low-intensity resistance exercise with the reduction of muscle blood flow. European Journal of Applied Physiology. 2005; 95(1): 65–73.


36. Kim YS, Park EK, Ahn YC, Park CM, Jeon BH. Changes of Muscle Insulin-like Growth Factor-I and Concentrations of Inflammatory Cytokines in Rat Skeletal Muscle Following Denervation and Diabetesinduced Atrophy. Asian J Kinesiol. 2016; 18(2): 93–103.

37. Laurentino GC, Ugrinowitsch C, Roschel H, et al. Strength Training with Blood Flow Restriction Diminishes Myostatin Gene Expression. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise. 2012; 44(3): 406–412.


38. Schwarz NA, McKinley-Barnard SK, Spillane MB, Andre TL, Gann JJ, Willoughby DS. Effect of resistance exercise intensity on the expression of PGC-1α isoforms and the anabolic and catabolic signaling mediators, IGF-1 and myostatin, in human skeletal muscle. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016; 41(8): 856–63.


39. Jürimäe J, Hills AP, Jürimäe T. Cytokines, Growth Mediators and Physical Activity in Children during Puberty. Medicine and Sport Science; 2010.